Schoolbegin ⎼ School News in Nigeria & Free Guide: An Overview
Schoolbegin delivers crucial Nigerian school resumption updates, alongside a comprehensive free guide, assisting parents and students navigate the 2024/2025 academic year effectively.
The Nigerian school calendar is traditionally structured around a three-term academic session, though specific dates can vary significantly between states and even schools. Schoolbegin aims to provide clarity amidst this complexity. Typically, the academic year begins in September/October with the First Term, followed by a mid-term break in December, and resumption in January for the Second Term.
The Second Term usually extends until late March or early April, punctuated by another mid-term break. The Third Term commences in April/May, concluding with examinations in July/August before a lengthy holiday. However, factors like public holidays, unforeseen circumstances – such as health crises like the recent Ebola concerns – and government directives can lead to adjustments. Staying informed about state-specific announcements is crucial for parents and students, and Schoolbegin is dedicated to delivering those updates promptly.
Understanding School Resumption Dates in Nigeria
Determining school resumption dates in Nigeria requires careful attention, as a nationally standardized date doesn’t exist. Each state government, and sometimes individual schools, announce their specific schedules. Schoolbegin focuses on consolidating this fragmented information for easy access. Recent announcements indicate Jigawa State schools will resume on Monday for the third term of the 2024/2025 session.
Kano State has set January 5th, 2025, as the resumption date for boarding students. These dates are subject to change, particularly due to ongoing health concerns, like the recent Ebola cases prompting potential review of earlier schedules. Parents and guardians must actively seek updates from official sources and utilize resources like Schoolbegin to remain well-informed and prepared for a smooth transition back to school.

Regional School Resumption Updates (2024/2025)
Schoolbegin provides timely, state-specific resumption details for the 2024/2025 academic year, including updates from Jigawa and Kano states, and potential health-related delays.
Jigawa State School Resumption
Schoolbegin reports that the Jigawa State Ministry of Basic Education has officially announced the resumption date for all public and private schools within the state. Academic activities are scheduled to recommence on Monday, marking the official start of the 2024/2025 third term. This announcement provides clarity for students, parents, and educators alike, allowing for necessary preparations before the term begins.
Parents are advised to ensure their children are equipped with all required learning materials and are mentally prepared to return to school. School administrators are expected to ensure a safe and conducive learning environment for all students. Further details regarding specific school schedules and any additional guidelines will be communicated directly by individual schools. Schoolbegin will continue to monitor and provide updates as they become available.
Kano State School Resumption
Schoolbegin confirms that the Kano State Government has declared Sunday, January 5th, 2025, as the official date for boarding students to resume at all public and private primary and secondary schools. This resumption signals the commencement of the new term, offering a defined timeline for families to finalize arrangements.
Day students are expected to resume shortly after, with specific dates to be announced by individual school administrations. Parents of boarding students are urged to make necessary travel arrangements to ensure their children arrive safely on the designated date. Schools are preparing to welcome students back with updated schedules and learning plans. Schoolbegin will continue to provide updates regarding resumption dates for day students and any further announcements from the Kano State Government.
Potential Delays Due to Health Concerns (Ebola Virus)
Schoolbegin reports growing concerns regarding potential disruptions to the school calendar due to ongoing Ebola Virus cases within Nigeria. The House of Representatives is actively seeking a review of the initially proposed September 22nd resumption date for primary and secondary schools nationwide.
This review stems from a desire to prioritize student and staff safety, acknowledging the serious health risks posed by the virus. While no definitive decision has been made, the possibility of further delays looms, pending expert advice and government assessment of the evolving situation. Schoolbegin will closely monitor developments and provide timely updates to parents and students, ensuring everyone remains informed about any changes to the school resumption schedule. Public health remains paramount.
Federal Government Guidelines on School Resumption
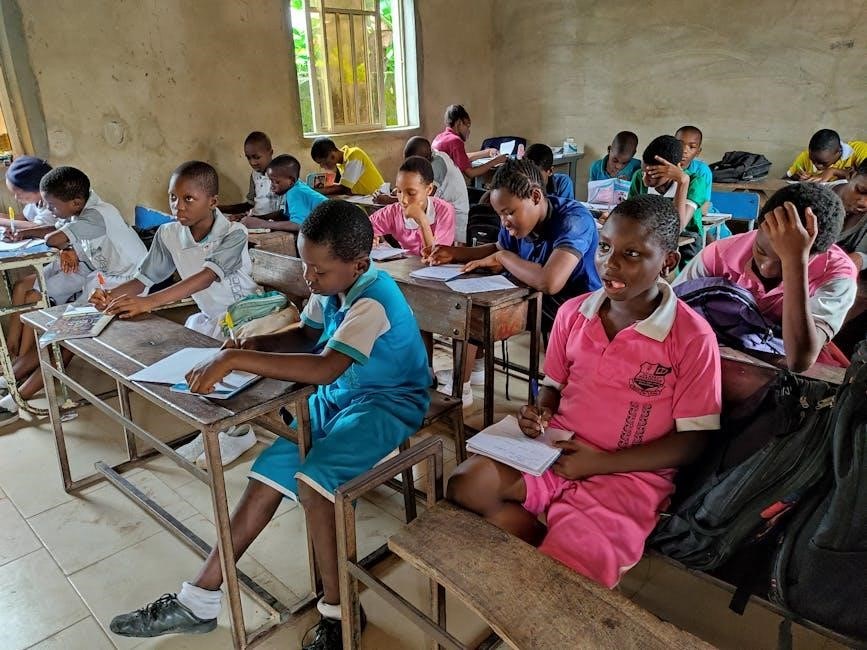

Schoolbegin understands the Federal Government is formulating comprehensive guidelines to ensure a safe and orderly school resumption across Nigeria. These guidelines are expected to encompass strict adherence to health protocols, including mandatory temperature checks, provision of hand sanitizers, and enforcement of social distancing measures within classrooms and school premises.
Furthermore, the government is likely to emphasize regular disinfection of school facilities and the implementation of robust hygiene practices. Schoolbegin anticipates directives regarding phased resumption strategies, potentially prioritizing final-year students initially. Detailed communication regarding these guidelines will be disseminated through the Ministry of Education and relevant agencies. Parents and schools are urged to stay informed and comply fully with these directives to safeguard the well-being of the school community.

Key Dates for the 2024/2025 Academic Session
Schoolbegin provides a detailed calendar outlining crucial dates: term resumption, mid-term breaks, and examination schedules, ensuring students and parents stay organized effectively.
First Term Resumption Dates (State-by-State)
Schoolbegin understands the complexities of coordinating school resumption across Nigeria’s diverse states. While a nationwide, uniform date is absent, we compile verified information to assist parents; Currently, Jigawa State has announced Monday as the first term resumption date for all public and private schools, initiating the 2024/2025 academic year. Kano State differs, setting Sunday, January 5th, 2025, specifically for boarding students in both public and private primary and secondary institutions.
Resumption dates for other states are still pending official announcements, and Schoolbegin is dedicated to providing updates as they become available. Parents are strongly advised to confirm dates directly with their children’s schools, as regional variations and unforeseen circumstances can influence schedules. We aim to be your central resource for navigating these crucial first-term commencement details.
Mid-Term Break Dates
Schoolbegin recognizes the importance of mid-term breaks for student wellbeing and academic rejuvenation. However, specific mid-term break dates for the 2024/2025 academic session remain largely unconfirmed across Nigerian states as of today, November 28th, 2025. Typically, these breaks fall approximately halfway through each term, offering students a short respite from intensive learning.
Given the varied resumption dates already announced – Jigawa State commencing on Monday and Kano State on January 5th, 2025 – mid-term breaks will likely follow a similar pattern of state-specific scheduling. Parents should anticipate announcements from individual schools and state ministries of education regarding these crucial dates. Schoolbegin will diligently update this section as official information becomes accessible, ensuring you have a clear overview of planned mid-term breaks.
Second Term Resumption Dates
Schoolbegin understands the need for clarity regarding second term resumption dates across Nigeria. As of November 28th, 2025, official dates are still pending for most states, following the staggered resumption for the third term already announced in Jigawa and Kano. Kano State boarding schools are set to resume January 5th, 2025, potentially indicating a similar timeframe for other states’ second term commencement.
However, the ongoing concerns surrounding Ebola Virus cases and potential reviews of the academic calendar by the House of Representatives introduce an element of uncertainty. Parents and students are advised to regularly check with their respective schools and state ministries of education for confirmed dates. Schoolbegin is committed to providing timely updates as they become available, ensuring a smooth transition back to school for the second term.
Third Term Resumption Dates & Examination Schedules
Schoolbegin reports that Jigawa State has already announced the commencement of the 2024/2025 third term, with schools resuming on Monday, November 28th, 2025. Kano State follows closely, with boarding schools slated to reopen on January 5th, 2025, marking the start of their third term. Examination schedules for the third term are currently being finalized by individual schools and state education ministries.
However, the potential for further delays due to ongoing Ebola Virus concerns remains a factor. The House of Representatives is considering a review of existing resumption dates, which could impact the third term timeline. Parents should proactively contact their children’s schools for specific examination dates and any potential adjustments to the academic calendar. Schoolbegin will continue to monitor and relay updates as they unfold.

Free Guide: Preparing for School Resumption
Schoolbegin’s free guide offers essential preparation tips, covering finances, uniforms, health protocols, and transportation, ensuring a smooth transition back to school for Nigerian students.
Financial Preparation: School Fees & Expenses
Budgeting for school resumption requires careful planning. Parents should ascertain exact school fees well in advance, factoring in potential increases. Beyond tuition, anticipate expenses like textbooks, uniforms, stationery, and examination fees. Consider costs associated with extra-curricular activities, such as sports or clubs.
Explore payment plan options offered by the school to alleviate immediate financial strain. Start saving early and create a dedicated school fund. Don’t forget to budget for transportation costs – fuel, bus fares, or potential boarding expenses.
Look into potential financial assistance programs or scholarships to offset costs. Prioritize essential items and explore affordable alternatives where possible. A detailed financial plan minimizes stress and ensures your child’s educational journey isn’t hampered by monetary concerns.
Uniforms & School Supplies Checklist
A comprehensive checklist is vital for smooth school resumption. Begin with uniforms – shirts, trousers/skirts, socks, belts, and shoes – ensuring proper sizing for growth. Compile a list of required textbooks, notebooks, pens, pencils, erasers, rulers, and mathematical sets. Don’t overlook specialized supplies like art materials or science lab equipment.
Check if the school provides a specific supply list; adhere to it closely. Consider a durable backpack and lunchbox. Label all items clearly with your child’s name and class. Prioritize quality over cost for items used frequently, like shoes and backpacks.
Involve your child in the shopping process to foster responsibility. A well-prepared student feels confident and ready to learn. Regularly review and replenish supplies throughout the term to maintain optimal learning conditions.
Health & Safety Protocols for Students
Prioritizing student wellbeing is paramount. Given ongoing health concerns like the Ebola Virus, strict adherence to safety protocols is crucial. Ensure your child is fully vaccinated according to national guidelines. Teach and reinforce frequent handwashing with soap and water, or use alcohol-based sanitizers.
Encourage the use of face masks in crowded settings, as advised by health authorities. Pack a personal hygiene kit containing tissues, hand sanitizer, and a small first-aid kit. Educate children about social distancing and responsible coughing/sneezing etiquette.
Report any illness immediately to the school authorities. Stay informed about school-specific health policies and cooperate fully with any implemented measures. A healthy student is a successful student – proactive health management is key.
Transportation Logistics for School Commuting
Safe and reliable transportation is essential for consistent school attendance. Carefully plan your child’s commute, considering options like school buses, private vehicles, or public transport. If using public transport, ensure they understand road safety rules and are aware of their surroundings.

For private vehicles, confirm the driver is licensed and practices safe driving habits. Establish clear pick-up and drop-off locations, prioritizing safety and minimizing congestion. If your child walks, designate a safe route and encourage walking with a buddy.
Communicate regularly with the school regarding transportation arrangements. Factor in potential traffic delays, especially during peak hours. A well-planned commute reduces stress and ensures your child arrives at school ready to learn.

Navigating the Nigerian Education System
Nigeria’s education encompasses primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, each with unique structures and requirements; understanding these stages is vital for student success.
Primary Education Structure
Nigeria’s primary education typically spans six years, divided into Lower Primary (Years 1-3) and Upper Primary (Years 4-6). This foundational stage focuses on basic literacy, numeracy, and life skills, preparing children for secondary education. The curriculum, largely determined by state governments, generally adheres to the National Policy on Education guidelines.
Pupils are usually admitted around the age of six, though this can vary. Core subjects include English Studies, Mathematics, Nigerian Languages (Hausa, Igbo, Yoruba, depending on the region), and basic Science and Social Studies. Assessment is continuous, with examinations at the end of each term and a primary school leaving certificate examination at the completion of Year 6. Successful completion is a prerequisite for entry into Junior Secondary School, marking a crucial transition in a child’s educational journey.
Secondary Education Structure (Junior & Senior)
Nigeria’s secondary education is divided into two phases: Junior Secondary School (JSS), lasting three years (Years 7-9), and Senior Secondary School (SSS), also three years (Years 10-12). JSS provides a general education across a broad range of subjects, building upon the primary school foundation. Core subjects include English, Mathematics, Sciences, Social Studies, and a Nigerian Language.
Upon completion of JSS, students undertake the Basic Education Certificate Examination (BECE). SSS offers a more specialized curriculum, allowing students to choose subjects aligned with their future academic or career goals. The Senior Secondary School Certificate Examination (SSCE), administered by various examination bodies (NECO, WAEC), is crucial for university admission. Successful completion of SSS and the SSCE are essential for accessing tertiary education opportunities.
Tertiary Education Options
Nigeria’s tertiary education landscape is diverse, encompassing Universities, Polytechnics, and Colleges of Education. Universities offer degree programs – Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral – across various disciplines, including Arts, Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Admission is highly competitive, typically based on SSCE results and performance in the Unified Tertiary Matriculation Examination (UTME).
Polytechnics focus on practical, technical, and vocational training, awarding National Diplomas (ND) and Higher National Diplomas (HND). Colleges of Education specialize in teacher training, producing qualified educators for primary and secondary schools. Increasingly, private tertiary institutions are emerging, offering alternative educational pathways. Students should carefully research programs and institutions to align with their career aspirations and academic strengths.

Recent Developments in Nigerian Education Policy
Recent policies prioritize improved access, quality, and relevance within Nigeria’s education sector, addressing challenges and integrating technology for enhanced learning outcomes.
Government Initiatives for Improved Education
The Nigerian government is actively implementing several initiatives to bolster the education sector, recognizing its pivotal role in national development. These efforts encompass increased budgetary allocations towards education, aiming to enhance infrastructure and resource availability across schools nationwide.
Furthermore, teacher training programs are being prioritized to improve the quality of instruction and pedagogical approaches. The government is also focused on expanding access to education, particularly in underserved communities, through scholarship programs and conditional cash transfers.
Digital literacy initiatives are gaining momentum, with efforts to integrate technology into classrooms and provide students with essential digital skills. The Universal Basic Education (UBE) program remains a cornerstone, striving to ensure free and compulsory basic education for all Nigerian children. These combined strategies demonstrate a commitment to building a more robust and equitable education system;
Challenges Facing the Nigerian Education Sector
Despite governmental efforts, the Nigerian education sector grapples with significant challenges. Inadequate funding remains a persistent issue, hindering infrastructure development, teacher recruitment, and resource provision. This is compounded by regional disparities, with rural areas often lacking basic educational facilities.
Security concerns, including the threat of school abductions, disrupt learning and create a climate of fear. The recent Ebola Virus outbreaks also pose potential risks, necessitating careful health protocols and potentially leading to school closures.
Furthermore, a shortage of qualified teachers, coupled with inadequate training, impacts the quality of education. Outdated curricula and a lack of access to technology further exacerbate these issues. Addressing these multifaceted challenges is crucial for unlocking the full potential of Nigeria’s youth and fostering sustainable development.
The Role of Technology in Nigerian Schools
Technology is increasingly vital in modernizing Nigerian education, offering solutions to long-standing challenges. Online educational platforms are expanding access to learning resources, particularly in underserved areas, bridging geographical gaps and providing supplementary materials.
However, widespread adoption faces hurdles. Limited internet connectivity, particularly in rural communities, and a lack of affordable devices hinder progress. Teacher training in utilizing digital tools is also essential to maximize the benefits of technology integration.
Despite these obstacles, the potential is immense. Technology can enhance teaching methods, personalize learning experiences, and prepare students for the demands of a digital world. Government initiatives and private sector investments are crucial to overcome the existing barriers and unlock the transformative power of technology in Nigerian schools.

Resources for Parents & Students
Schoolbegin provides links to online educational platforms, scholarship databases, and vital government websites, empowering parents and students with essential resources for success.
Online Educational Platforms
Schoolbegin recognizes the growing importance of digital learning in Nigeria. Numerous online platforms offer supplementary educational resources for students of all levels. Platforms like Coursera and edX provide access to university-level courses, beneficial for senior secondary students preparing for tertiary education.
For primary and junior secondary students, platforms such as Khan Academy offer free, comprehensive lessons in mathematics, science, and other core subjects. Local Nigerian platforms are also emerging, providing content tailored to the Nigerian curriculum. These include Passnownow, which focuses on past questions and exam preparation, and Schooolwave, offering virtual classroom experiences.
Parents should explore these options to supplement their children’s learning and provide additional support, especially during school closures or as a means of reinforcing classroom lessons. Utilizing these platforms can significantly enhance a student’s academic performance and prepare them for future challenges.
Scholarship Opportunities
Schoolbegin understands the financial challenges many Nigerian families face in funding education. Fortunately, numerous scholarship opportunities exist to support students at various levels. The Nigerian government offers scholarships through the Federal Ministry of Education, often targeting students excelling in specific fields.
Private organizations and foundations also provide substantial financial aid. The MTN Foundation Scholarship Scheme is a well-known example, supporting students in tertiary institutions. Additionally, international organizations like the Shell Petroleum Development Company (SPDC) offer scholarships focused on science and engineering.
Students and parents should actively research and apply for these opportunities. Websites like ScholarshipRegion and Opportunities For Africans compile lists of available scholarships. Early preparation of application materials and meeting deadlines are crucial for success. Securing a scholarship can significantly alleviate the financial burden of education.
Relevant Government Websites & Contacts
Schoolbegin provides key governmental resources for Nigerian students and parents seeking reliable information. The Federal Ministry of Education website (www.education.gov.ng) is the primary source for national education policies, updates, and announcements regarding school calendars.
State Ministries of Education websites offer localized information; for example, Jigawa State’s Ministry of Basic Education and Kano State’s Ministry of Education. Contacting these ministries directly can provide specific details on resumption dates and guidelines.
The National Universities Commission (NUC) website (www.nuc.edu.ng) is vital for tertiary education information. For health-related concerns, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) (www.ncdc.gov.ng) provides updates on potential health risks impacting school schedules. Utilizing these official channels ensures access to accurate and timely information.
Staying Updated on School News
Schoolbegin recommends utilizing reliable Nigerian news sources, engaging in social media forums, and checking school communication channels for timely updates and information.
Reliable News Sources for Nigerian Education
Staying informed about the Nigerian education sector requires accessing trustworthy and up-to-date news platforms. Schoolbegin suggests prioritizing national newspapers like The Guardian, This Day, and The Nation, which consistently feature education-related reports.
Online news portals such as Premium Times and Sahara Reporters often provide detailed coverage of educational policies and developments. For specialized education news, explore platforms like EduCeleb and School News Nigeria.
Furthermore, regularly checking the official website of the Federal Ministry of Education (www.education.gov.ng) is crucial for accessing official announcements, circulars, and policy updates directly from the source. Remember to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and a comprehensive understanding of the evolving educational landscape in Nigeria.
Social Media Groups & Forums
Schoolbegin recognizes the power of social media for real-time updates and community discussions regarding Nigerian education. Facebook groups dedicated to school resumption dates, like “Nigeria School Resumption News” and groups specific to individual states, are valuable resources.
Twitter (now X) provides quick access to breaking news and announcements from education stakeholders; follow relevant handles like the Federal Ministry of Education and prominent education journalists.
Online forums, such as Nairaland’s education section, host discussions where parents and students share information and experiences. However, exercise caution and verify information obtained from these platforms, as accuracy can vary. Active participation and responsible sharing contribute to a well-informed community, ensuring everyone stays connected and prepared.
School Communication Channels (SMS, Email, Websites)
Schoolbegin emphasizes the importance of direct communication from schools. Most Nigerian schools utilize SMS messaging to quickly disseminate urgent information, such as resumption dates or unexpected closures. Regularly check your registered mobile number for these alerts.
Email remains a primary channel for detailed announcements, circulars, and academic updates. Ensure your email address is current with the school administration. Furthermore, consistently visit the school’s official website – a central hub for calendars, policies, and important notices.
Parent-teacher associations (PTAs) often have dedicated communication groups. Proactive engagement with these channels guarantees you receive timely and accurate information, fostering a strong school-family partnership.